


| Vanteksp.com |
| 日本語 Japanese |
English 英語 |
中文 Chinese |
 |
 |
 |
| Top | About us | Products | Online Shop (refurbishing) |
News | Contact |
| Green Banana Resistant Starch | ||||
Traditionally, starch was considered to be well digested in the small intestines. However, in 1980's some scientists discovered that there are starches which are not digested in the small intestine but reach the large intestine intact, and named it "resistant starch". More researches have studied thereafter, and found the starch exhibits many beneficial effects on the digestive and colonic systems in addition to the resistance to digestion. The resistant starch is now one of the most notable food materials in health food and food industries. In 1992, EUREST defined the resistant starch as "starch and starch degradation which are not digested in the small intestine. Today, some countries classified resistant starch as a dietary fiber. |
|||
| Classification of Resistant Starch | ||||
| There are many kinds of starches which are not digested and absorbed. Currently, the starches are classified in the following four types. | |||
| R S 1 | Starches physically protected with the hard cell walls. (e.g. grains) | |||
| R S 2 | Starches having resistant structural granules naturally. (e.g. green bananas) | |||
| R S 3 | Starches retrograded by heating and cooling. (e.g. cooked rice) | |||
| R S 4 | Starches modified chemically. (e.g. acetylated starch) |
| Green Banana and Resistant Starch | ||||
| There exist many plants containing resistant starch in the nature. Among others, green banana has been widely noticed as it is well known that abundant in resistant starch. | |||
 Green banana |
Resistant starch exist in the Nature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bananas, an ancient and much loved fruit, are one of the four world major crops, with global production at around 100 millions of tons annually. Banana is widely grown in the tropical and subtropical areas in the neighborhood of the equator, so called "banana belt". Although it has been well known that banana starch exists in green banana has very unique health functions in additon to its physical properties, it has not been utilized due to some difficulties in extraction of high quality banana starch from green bananas. |
 Banana growing areas "banana belt" |
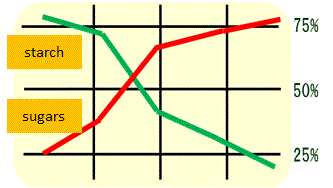
| Green color of banana, when harvested, gradually turns to yellow by the enzymes inherent, and the starch is degraded into sugars in parallel. Accordingly, use of green banana as the starting materials is needed for efficient extraction of banana starch. | |||
| Time course change of banana | |||
 |
 |
||
| General Properties of Green Banana Resistant Starch | ||||
| Major component of banana starch is so called "resistant starch"
which resists digestion in the small intestine of healthy humans. Although
starch is used as a major energy source, there is an increasing desire
for starch with no or less energy among health conscious people. Green
banana resistant starch is a new natural functional food ingredient developed
to meet such the demand. |
|||
| Basic properties of banana starch |  |
|||||||||||||
|
| Among others, the most notable property of banana starch is "the resistance to digestion". While other common starches are well degestible, banana starch is not digestible. Accordingly, banana starch with its all-purpose use as a starch just like other common starches could be a quite unique food ingredient with the various health functions. |
Nutritional Facts of Banana Starch
|
| Lot #150119 tasted by Japan Food Research Labs. |
| >>> Page Top |
| Health Functions of Resistant Starch | ||||
Resistant starth is expected to provide the following health functions. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Low GI and Insulin Resistant Effects |
| The carbohydrates in bananas change to digestible from non-digestible as
they are ripening. GI of yellowish (ripened) banana is 55-65 (medium GI),
while that of green (under ripened) banana is 30-40 (low GI). It has been reported that resistant starch is effective at lowering blood glucose levels and improves insulin sensitivity. |
|||
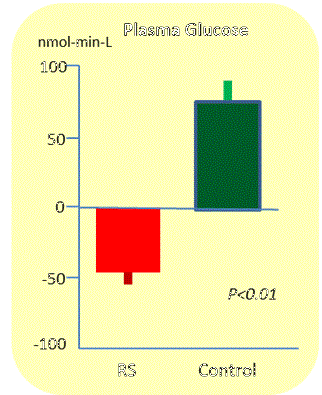 Change in Plasma Glucose until 5 hours after RS intake |
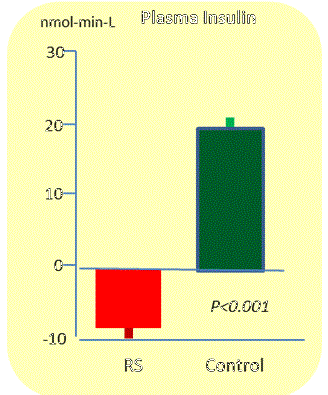 Change in Plasma Insulin until 5 hours RS intake |
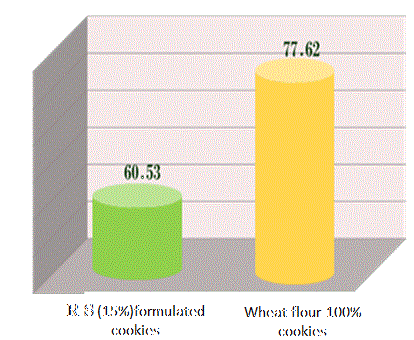 Change in GI after intake of RS formulated cookies |
||
| Subject No;10 healthy subjects(male5.female5) RS :50g of RS mixed 500ml fruit syrup Control:50g of starch mixed 500ml fruit syrup |
Source: resistant starch: the effect on postprandial glycemia, hormonal response, and satiety Anne Raben, Arne Astrupet al., Am J Clin Nutr 1994;60:544-51 | Alejandro Aparicio-Saguilon etc. Institute Technologico de Acupulco, Mexico, 15 July 2006 |
| Changes in body weight and BMI after intake of BS in diabetic patients | ||||
Effects on RS on body weight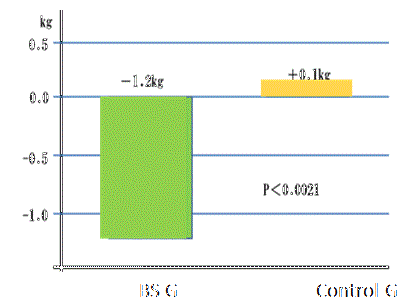 |
Effects on RS on BMI 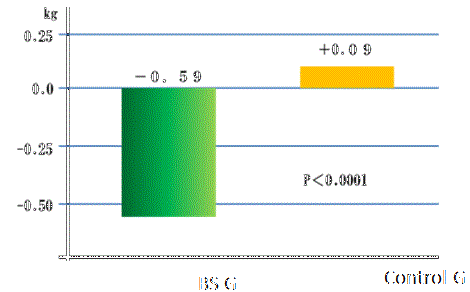 |
Test Period: 1 month daily amount 0.3 g/kg ob body weight of BS. | ||
| Jorge L., Ble-Castillo et al., Universidad Juarez Autonoma, Mexico, Feburary 17, 2010 |
| European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) examined the proposed claim, and approved the claim "replacement of digestible starch with resistant starch in high carbohydrate foods cdecreases postprandial blood glucose levels. (EFSA 2011) | |||
| Dietary Fiber like Effects |
| Resistant starch acts as both soluble and insoluble dietary fibers. | |||
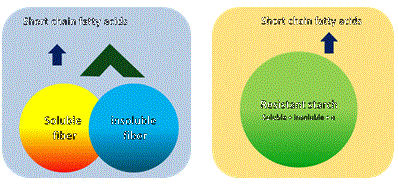 |
Comparison of Dietary Fiber and Resistant Starch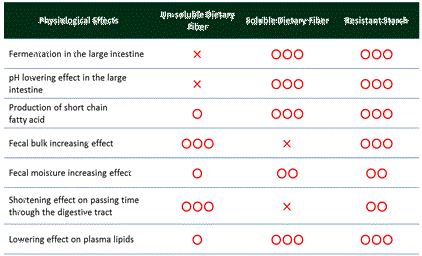 |
||
| Starch, a macromolecular substance, exhibits the effects of insoluble dietary fiber and at the same time produces beneficial short chain fatty acids. | Frontier of Luminacoides Research: T. Hayakawa, T.Oku Kenpakkusha 2010 p233-245 |
| <Normalization of Bowel Movement> Insoluble dietary fiber is less digestible by intestinal microbes, and has water-keeping property which leads well stool formations. Soluble dietary fiber has strong swelling power, therefore, forms soft bulky stool. THe bulky soft stool in the colon stimulates colonic movement resulting in very smooth defecation. Resistant starch has both benefits. |
|||
| There is the report showing that significant effects on intestinal pH and stool volume were observed after intake of 40g/day of RS for 3 weeks in 11 healthy subjects. (JP Phillips et al., 2009) | |||
Effects of RS on intestinal pH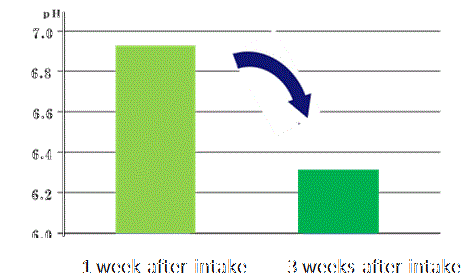 |
Effects of RS on stool volume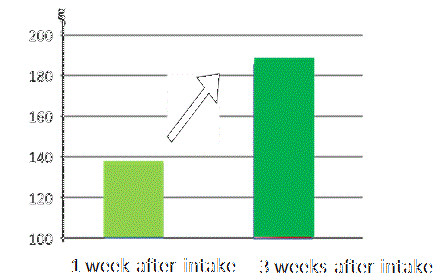 |
||
| JP Phillips, JG Muir, A Birkett, ZXIu, GP Jones, KO Dea and GP Young Author Affiliations, School of Nutrition and Public Health, Deakin University, Malvern, Australia |
| In the study of RS given children with Shigellosis infection, significant effects were shown in stool volume, stool frequency and excretion of blood. (Robbani, GH, MD et al, 2009) | |||
Effects on mucous stool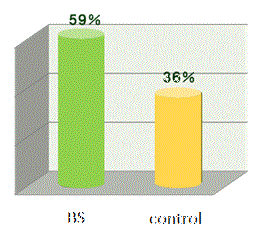 |
Effects of RS on stool frequency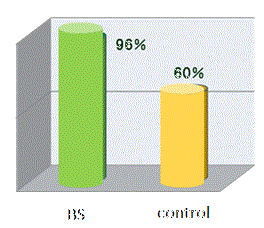 |
Effects of RS on normalizatin of stool volume 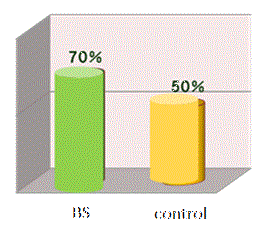 |
||
| Rabbani, G.H, MD et al., Pediatric infec. Disease Jou., May 2009, Vol.28, pp 420-425, Effects of banana starch on stool volume, frequency and excretion of blood in 73 children with sever Shigellosis infection |
| Supporting Effects on Colonic Health |
| Resistant starch is fermented by the intestinal microbes. When the microbes digest resistant starc, they form some beneficial metabolic products, particularly a fatty acid called butyrate, and also reduce the pH levels in the colon. The butyrate is the favored energy source of colon cells, and known to have many beneficial functions by stimulating and activating the cells that line the colon. Followings show the potential effects of butyrate reported in some medical publications. | |||
| Change after intake of 40g/day of RS for 3 weeks | |||
Change of Free Fatty Acids production 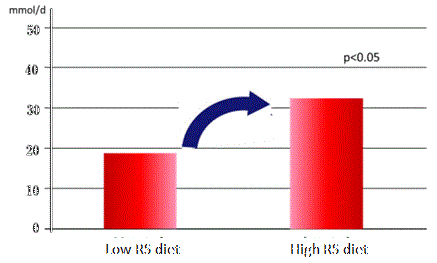 |
Change in pH 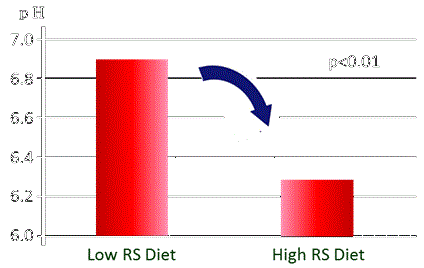 |
||||||||
| JP Phillips, et al, School of Nutrition and Public Health, Deakin University, Malvern, Australia. Am., J. Clin. Nutr. 1995,62:;121-30 Effect of resistant starch on fecal bulk and fermention-dependent events in humans | |||||||||
Roberto Canani, et,al., World Journal of Gastroenterology,Vol. 17 issue 12, Mar.2011., Potential benefical effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases |
Comparison of increase ratios of fatty acids after intake of RS 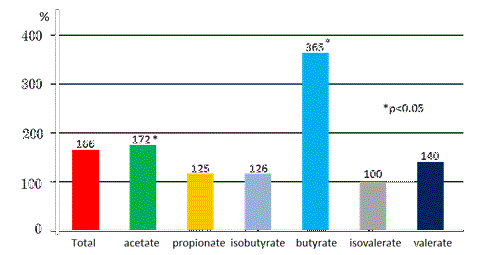 JP Phillips, JG Muir, A Birkett, ZXIu, GP Jones, KO Dea and GP Young Author Affiliations, School of Nutrition and Public Health, Deakin University, Malvern, Australia. |
| It is concluded that resistant starch contributes the health of host through a series of health supporting effects in the colon including enhanced fermentation, changes in the microflora composition. | |||
| Green banana resistant starch is now available in the market. As a new natural health-supporting food material, it is expected to be used in such health-oriented foods as diet foods, foods for diabetes and obese, foods for elderly people, medical foods as well as a natural health supplement. | |||
 |
GREEN BANANA Resistant Starch |
| >>> Page Top |
 |
| COPY RIGHT VANTEK CORPORATION 2014 ALL RIGHT RESERVED |